Introduction:-
In earlier chapters you have studied various optical phenomena like reflection, rebel refraction, interference, diffraction and polarization of light.
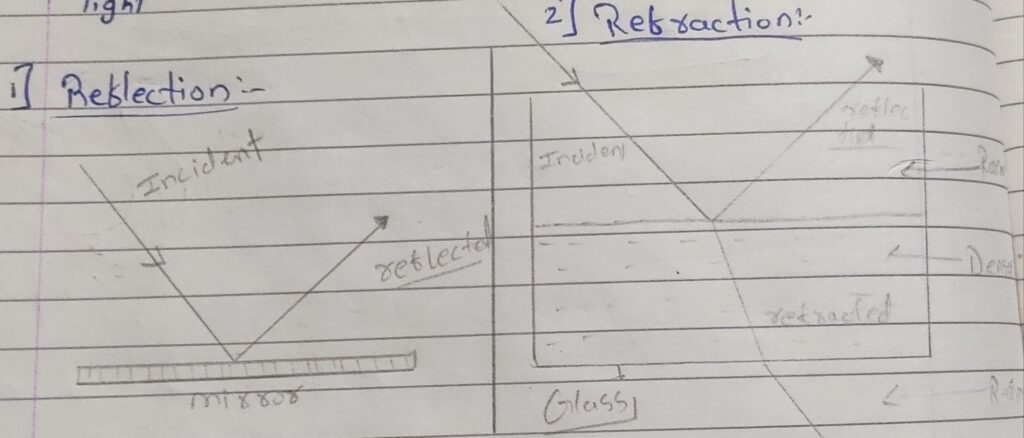
– light is electromagnetic radiation and most of the phenomenone mentioned have explained considering light os a Wave.
– we are also bomlar with the wave nature of electromagnetic radiation in other regions like x-ray, V-ray sinsrared ood ultraviolent sadiator.
– Electromagnetic radiation consist of oscillating electric and emagnetic fields.
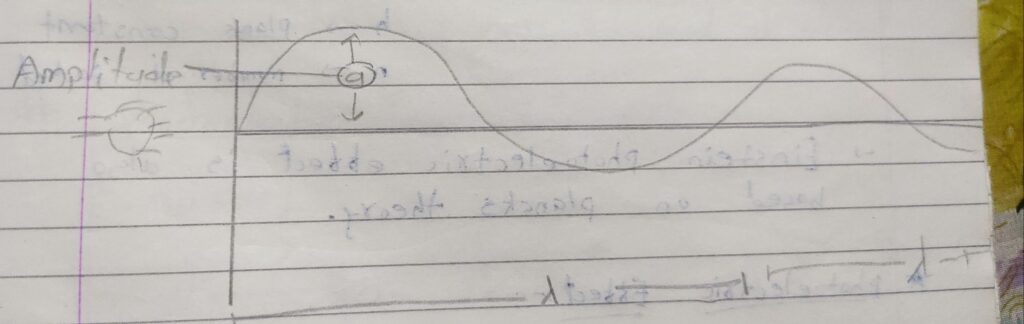
Amplitude period and frequency:-
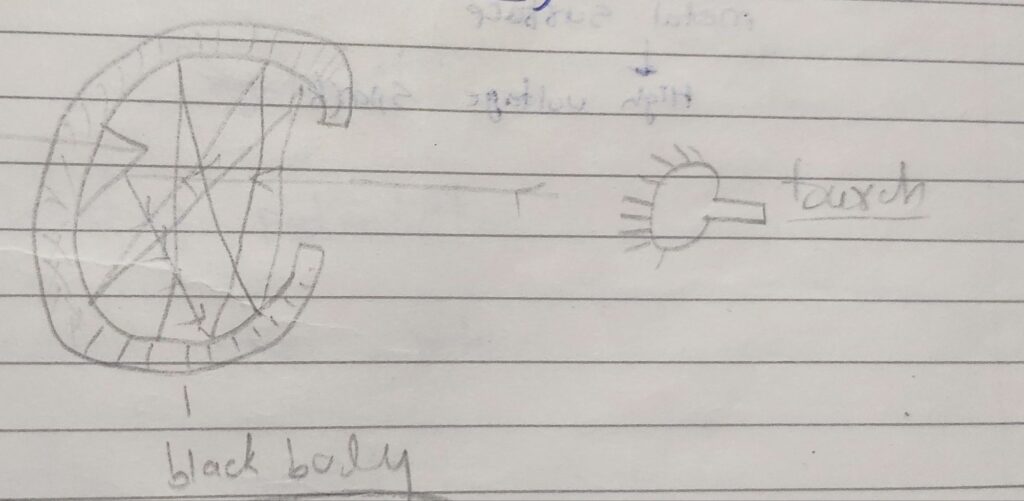
Spectrum of blackbody:-
Quantization of energy:-[scientist – plank]
1] energy emit – photon
2] higher frequency, higher photon
E=nhv
where, V= frequency
h= plank constant
n= number of packet
– Einstein photoelectric effect is also based plank theory.
photoelectric Effect:-
Heinrich Hertz
Ur light
metal surface
High voltage spark
Threshold frequency:-
-minimum frequency-for emit of element
Photoelectric experiment:-
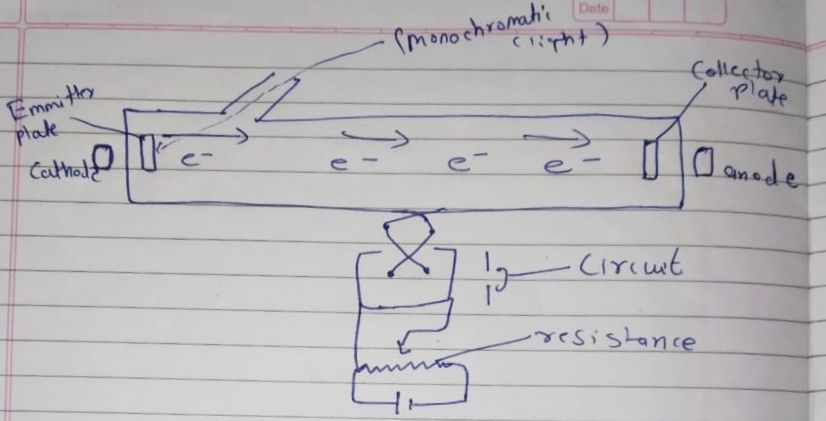
Acceleration potential:-
– accelerated the electron.
Restoring potential:-
-slow down the electron.
Wave Particle duality of electromagnetic radiation:-
– light have energy pockets called quanto
Further experiment Dethl.
quanta is accociated with momentum.
Experiment of crompton:-
photon associated with momentum.
all photons of same frequency having same
Photons are electrically neutral.
Photon Cen hove collision like particle.
→photon always moves with speed of light (3×18 ~/5)
These phenomena is termed A Wave- particle duality of electromagnetic radiation.
Photo cell:-
– Devise whid convert light energy into electrical energy.
– it is hypothesis .
De-Braglie hypothesis:-
– He used the properties of:-
frequency
Wave length
Energy (E)
Momentum (P)
use to detice Particle nature b light.
P = is momentum of particle with energy E.
P = e/c
where C = speed of light
P = E/C
p = h * 1/lambda
lambda = c/v
P = (hv)/c
therefore E C = hv * C
E = hv
P = h * d/c
u = e/h
For particle of mass ‘m’ ho having vekaty (v):
lambda = h/(mv)
= h/(m * sqrt(2E_{k}))
= h/m * sqrt(m/(2epsilon_{4})
E_{m} = qx
E_{A} = x hekse
A =h sqrt 1 28.m
lambda = h * sqrt(1/(2qvm)).
Devission and gemer experiment:-

