Introduction:-
– Light travel in straight line while travelling a uniform and homogeneous medium the path of light is called Ray of light.
– on encountering an interface with another medium a ray of light get raflected or refracted change its direction and moves along straight line
Light nature or nature of light:-
- Corpuscular nature
– newton (1642-1726) -light rs made of partical.
– Light partical – corpuscular- hard, elastic, massless.
– Source of light- emit- capsules- straight line – no external force.
– Corpuscles- elastic collision – reflaction.
– During refractions- Corpuscles & medium particle have different attractions force – change direction.
- Newton’s theory- predicted- light speed in dencer medium is higher than light speed in rarer midium.
- The study of optical phenomenon the light travel in straight line as a ray is called Ray optics.
Wave Nature:-
-physicist- c.huygen(1629-1695)-light is wave.
-Huygen assumed light to be a wave caused by vibration of the partical of the medium.
-light travel in hypothetically medium called ether is present everywhere including vacuum.
-no evidence – difficult to accept the concept.
-19th century, interference, diffraction and polarization- wave theory and Corpuscular theory.
-it was then accept as correct.
-wave theory showed- light speed dencer medium is smaller than rarer medium- light bends toward normals.
-the branch of optics shows wave Nature of light called wave optics.
Dual nature of light:-
1) wave Nature (2) partical nature
a) light as a wave:-
-light- electromagnetic waves.
-tiny oscillating electric and magnetic field – perpendicular.
-no medium required- travel through vacuum.
-electromagnetic wavelength- very smaller to larger i.e 10`15, femtometer to kilometer.
-visible light comprise of wavelength in 400-700nm range.
-different wavelength – i.e eyes- different colour.
-voilet having shortest and red having longest wavelength.
-white light mixture of different wavelength.
Huygen’s theory:-
- Primary and secondary source of light.
-sources of light- i.e sun, moon, star, bulb, etc.
-Classified as primary and secondary.
-primer sourcess – emit their own light – because.
- High temperature(i.e sun, star, etc)
- Effect of current(i.e tube light, etc)
- Chemical or nucleus reaction(i.e firecrackers)
-secondary sources- do not produce light of their own – recieve light from other sources – example. Moon, plant, object like humans, animals, plants etc.
Wave front:-
-drop a stone in water – ripples – generated – travel outword from point O.
-water partical – moves – up down – perpendicular surface.
-phase of waves – define by – State of motion of partical.
-two partical – same phase – State of motion same – same velocity and displacement – same distance from source.
-the lows of all the point having same phase at given instant tire is called wave Frost.
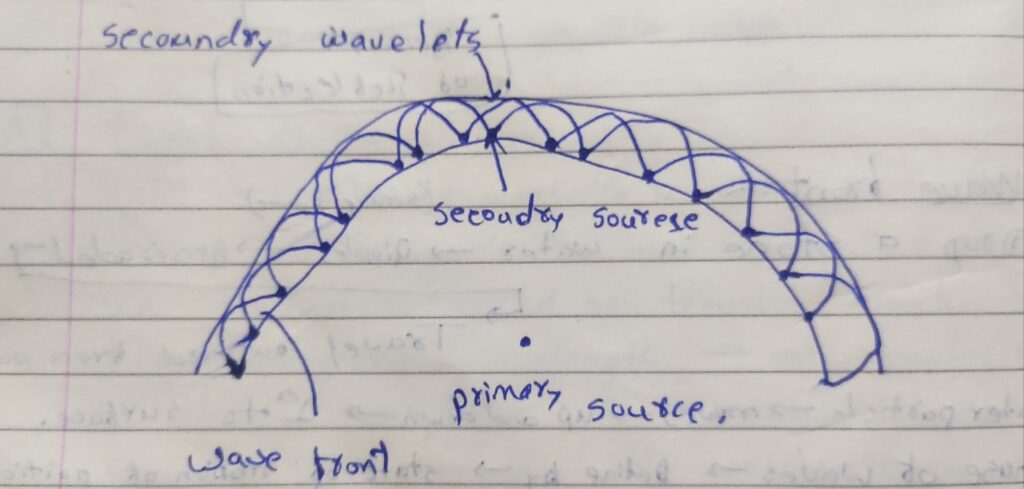
Huygen’s principle:
He assumed light as wave like water and secound wave.
Each points on the wave front act secoundry source of light emitting secondary light waves called wavelets [travel with light speed] Wavefronts.con of Wavelets be obtained by – envelopers
- There is no reason why bankward travelling. waves will not be effective.
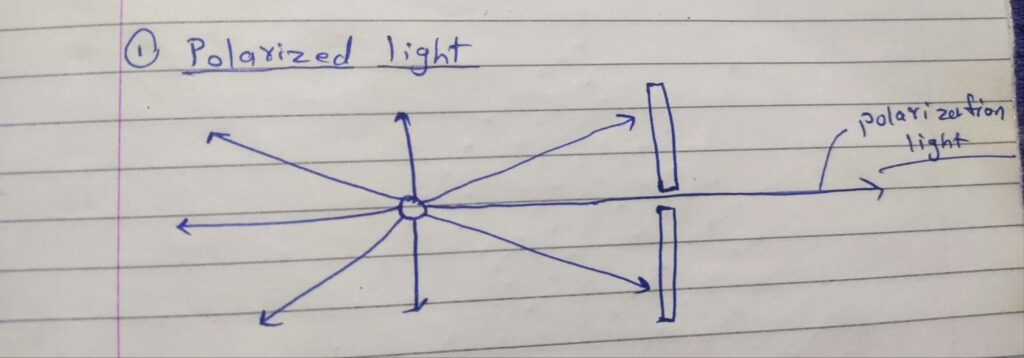
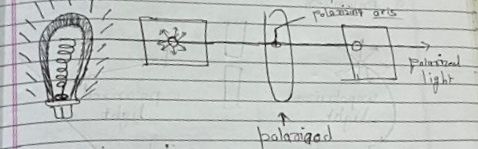
Polarization:-
1)Polarized light
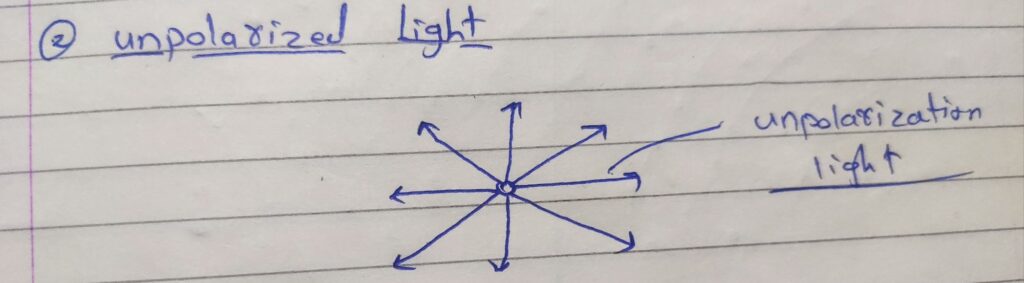
2)unpolarized
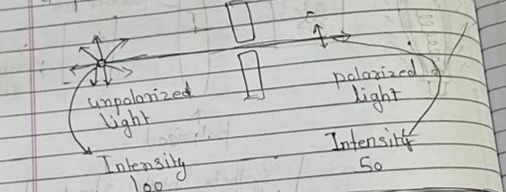
Intensity:-
-the intensity of an edues by a Palariza half un-pelazizard wave after or passing through
Polarization by Scattering:-
- when sunlight strikes ais molecules or oldest Particle in the atmosphere it changes its disection this is called Scattering Sky is blue because of angle between and in cindcattering and Scattering light is called angle of Scuttering.
polazization:-
the press of transformation of unpolarized light inte polarized light is known as polarization.
[Synthetic plastic shret which is used as polarized]
Polarizer:-
It optical filter that lets light waves of a specific polarization pass through while blocking light waves of other polarization
Interference:-
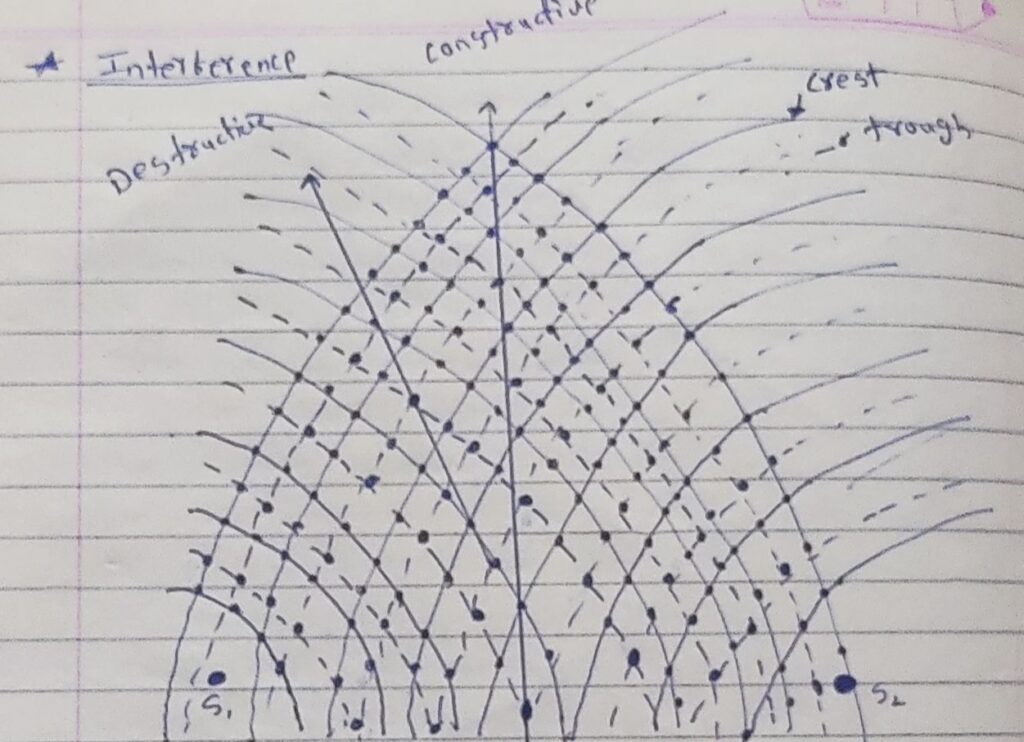
-first time Thomas joung [1773-1829] light 1801
Young double slit experiment:-
..
Fraunhofor diffraction:-
If the distance between primery source of light, and for viewing the diffraction pattern are very large the diffraction: diffraction in called fraunhofor diffraction.
Resolving power:- [scientist – renold]
Diffraction effect is most significant while discussing the resolving power of an optical instrument. The ability to distinguish two physically separated object two district object is resolving power known as
Example distance. two finger showing from lom or gon.
It is the minimum visual angle between twe object that con be resoled by that instrument. This minimum angle is. called limit of resolution. Reciprocal of the limit of resolving is called Resolving Power.
